What is Uveitis?
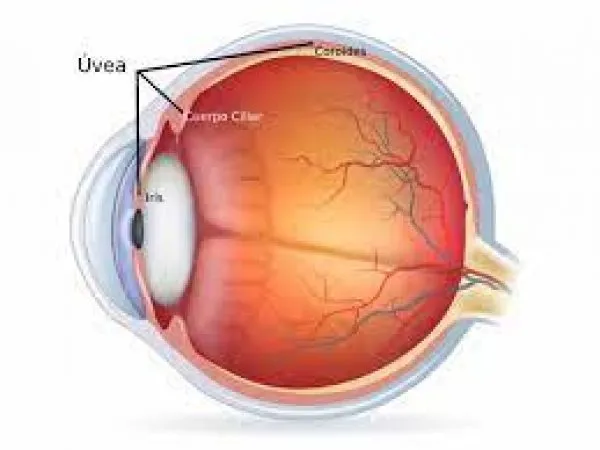
The Uvea is the part of an eye made up of blood vessels, the iris, the ciliary body, and the choroid. The Uvea is positioned between the sclera and retina. The progression of inflammation in the eyes causes the Uveal tissue to swell.
It has a significant effect on deteriorating the health of the lens, retina, optic nerve, and vitreous. In severe conditions, it might lead to vision loss and blindness. People of all ages can contract the Uvea eye disorder. The prevalence of the illnesses can be acute or chronic, depending on their advancement and the appropriate treatment to stabilize them. An individual can contract the reoccurrence of Uvea illness based on their health condition.
Types of Uveitis
- Anterior Uveitis: It is a condition when inflammation develops on the iris and ciliary body of the eye.
- Intermediate Uveitis: It is an eye condition where inflammation is observed in the ciliary body of the eye.
- Posterior Uveitis: The progression of inflammation is observed in the choroid of an eye
- Diffuse Uveitis: The occurrence of inflammation is seen in all parts of the Uvea.
Symptoms
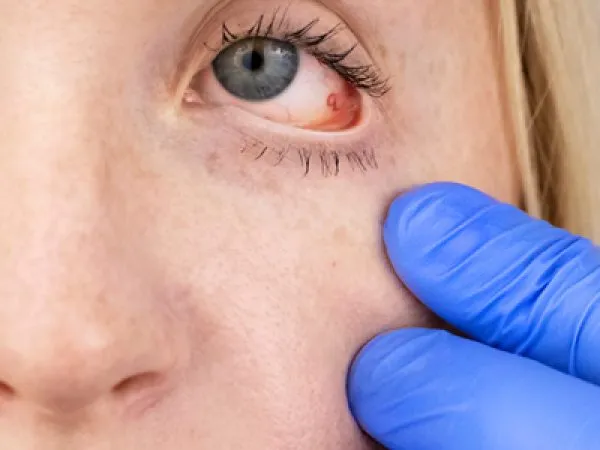
Uveitis can affect one or both eyes simultaneously. The progression of the symptoms can be aggressive.
Based on the type and severity of inflammation, the signs and symptoms vary. Eye Examination and its results are helpful in categorizing the type of Uveitis. Eye pain, blurred vision, eye redness, and sensitivity to light are the commonly experienced symptoms of acute anterior Uveitis. Blurred vision and eye floaters are signs of intermediate Uveitis. Vision loss is a sign of posterior Uveitis.
Causes
Tissue damage, viral infection, and the segregation of toxins are the major causes of inflammation. The advancement of inflammation leads to swelling and redness. It reduces the WBC, which fights against illnesses. The development of inflammation in the Uveal tissue advances Uveitis. Some of the primary causes of Uveitis are:
- Reduced autoimmunity
- Dark eye floaters
- Idiopathic
- Development of tumours and infection in the eyes
- Drugs (overdosage or proneness to allergy due to other medical reasons)
Uveitis Eye Check-up at Trinity
The diagnosis of Uveitis includes a thorough patient’s medical history and a detailed examination of the eye to record the findings.
Ancillary investigations and laboratory tests are conducted to examine the prevailing condition of infection and autoimmune disorder, which helps our ophthalmologists decide the appropriate Uvea treatment.
Eye examination includes
Eye Chart or Visual Acuity Test: This test measures whether a patient’s vision has decreased.
Ocular Pressure
- Slit Lamp Exam: It is a non-invasive procedure performed to diagnose the front and back parts of the eye.
- Dilated Fundus Examination: The pupil is widened (dilated) with eye drops, and then a light is shown through an instrument called an ophthalmoscope to noninvasively inspect the back, inside part of the eye.
Complications of Uveitis
In most cases, people with Uveitis experience chronic Uvea conditions. Cloudy cornea, cataracts, elevated eye pressure (IOP), glaucoma, and retinal detachment are the complications of Uveitis that are diagnosed when the disease prevails for a long time and the Uvea eye infection is untreated.
Our Eye Specialist diagnoses the Uvea condition precisely and provides appropriate treatment to stabilize the prevailing inflammation and eye pain, prevent the advancement of tissue damage, and restore the quality of vision.
Based on the Uveitis type and condition, our Ophthalmologists provide the treatment specified for it.
- Inflammation-Reducing Drugs: Prescribing eye drops with an anti-inflammatory medicine combination is the preliminary treatment procedure practiced to cure the prevailing Uveitis.
- Drugs that fight Bacteria or Viruses: Our Doctors prescribe medications, including antibiotics and antiviral medications, in addition to corticosteroids, based on the severity of the infection, to cure Uveitis caused by bacterial and viral infections.
- Drugs that affect the Immune System or Destroy Cells: When the Uveitis condition is due to damage to the immune system, our ophthalmologists prescribe drugs that stabilize the immune system, thereby preventing further progression and stabilizing the Uvea's health.
Uveitis Surgical Procedures at Trinity
- Vitrectomy: It is a surgical procedure performed to remove vitreous parts of the eyes to stabilize the condition.
- Time-Release Capsules: The procedure involved in implanting a medical device into the eyes serve the function of discharging medications. It is one of the treatment choices for people suffering from severe posterior Uveitis. The device injects medicines for up to three years to treat the condition. Cataracts and glaucoma are the possible side effects of undergoing this surgical treatment.
Anterior Uveitis Treatments
The advancement of muscle spasms in the iris and ciliary body can be prevented with the aid of eye drops.
The severity of inflammation can be controlled with the aid of eye drops that contain a medical combination of steroids.
Intermediate, Posterior, and Panuveitis Treatments
These Uvea eye conditions are treated with the aid of injects performed around the eye, oral medication, and time-release capsule surgical procedures. At Trinity, our Ophthalmologists perform a complete diagnosis and ensure the patient is free from other eye infections.
Routine eye check-ups are recommended for patients to monitor their progress and to prevent the side effects, including cataracts and glaucoma, of this treatment.
